Introduction
A facade refers to the front or exterior of something, particularly a building. The French spelling is façade, with a cedilla accent mark under the “c,” indicating the pronunciation of “s” instead of “k” — like “fuh-sod” rather than “fuh-kade.” Facade, or façade, is a frequently used term, making it useful to understand its definition and usage.

The Origin of Facade
The word “facade” has French roots, derived from the Italian word “facciata,” which means “face” or “front.” Over the years, it has come to signify the exterior appearance of a building. Interestingly, the term was initially used in the theater to describe the painted wall or flat surface that represented the location of a scene. Eventually, it found its way into the realm of architecture, becoming an integral part of the building’s design.
The Role of Facades in Architecture
Facades hold immense importance in architectural design, as they contribute to the overall aesthetics and functionality of a building. Let’s delve into the key roles that facades play in shaping the architectural landscape.

1. Visual Impact and Identity
The facade of a building is its first impression on visitors and passersby. It sets the tone and portrays the intended image of the structure, whether it’s a commercial building, a residential complex, or a cultural institution. A well-designed facade can instantly captivate people’s attention and create a lasting impact.
2. Protection and Sustainability
Beyond their aesthetics, facades serve as the protective shell of a building, shielding it from external elements such as weather, wind, and noise. They also contribute to the building’s energy efficiency, with advancements in facade technology allowing for better insulation and reduced energy consumption.
3. Structural Support and Safety
Facades play a vital role in providing structural stability to a building. They distribute the load of the structure evenly, ensuring its overall integrity. Additionally, facades incorporate safety features such as fire-resistant materials, escape routes, and emergency exits, ensuring the well-being of the occupants.
4. Communication of Design Principles
Architects often use facades to communicate their design principles and ideas. The facade can express the architect’s creativity, vision, and aesthetic sensibility. It may incorporate unique architectural elements, patterns, and materials that reflect the building’s purpose or cultural context.
Evolution of Facades
Over the centuries, the concept of facades has evolved to suit different architectural styles, technological advancements, and cultural influences. Let’s explore the major architectural movements that have shaped facades throughout history.

1. Classical Facades
Classical facades, notably seen in ancient Greek and Roman architecture, were characterized by their symmetrical design, grandeur, and use of columns. The facades of iconic structures like the Parthenon in Athens and the Colosseum in Rome still inspire architects today.
2. Gothic Facades
Gothic facades emerged during the medieval period and were characterized by their intricate ornamentation and verticality. Cathedrals such as Notre-Dame in Paris and Westminster Abbey in London epitomize the grandeur and elegance of Gothic architecture.
3. Renaissance and Baroque Facades
During the Renaissance and Baroque periods, facades became more elaborate, incorporating decorative elements such as sculptures, pediments, and balconies. The facades of buildings like the Palace of Versailles in France and St. Peter’s Basilica in Vatican City showcase the opulence and lavishness of this era.
4. Modern and Contemporary Facades
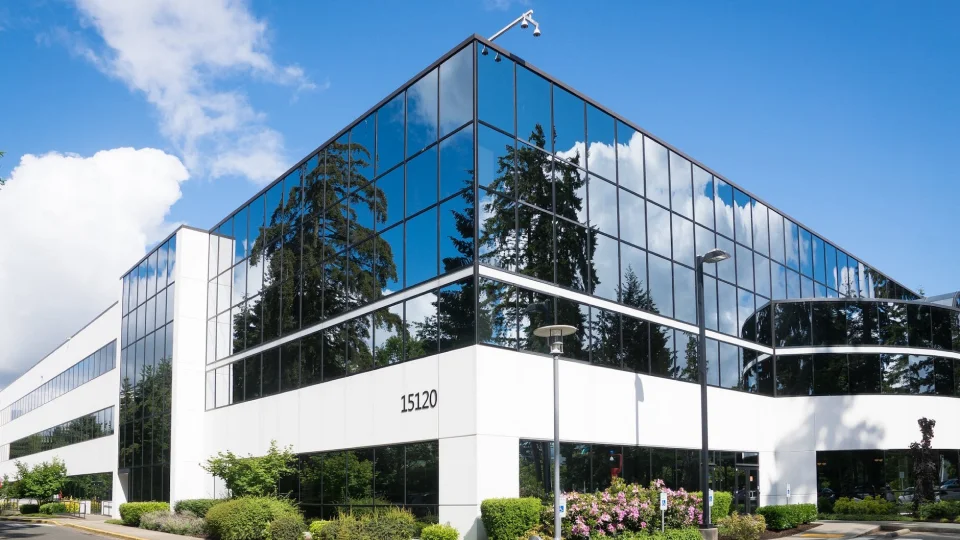
With the advent of modern architecture, facades underwent a radical transformation. Architects started experimenting with new materials such as glass, steel, and concrete, enabling the creation of sleek, minimalist facades. Iconic examples include the Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao, Spain, and the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, UAE.
The Future of Facades
In the era of sustainable architecture and technological advancement, facades are poised to undergo further innovation. Here are some emerging trends and possibilities for the future of facades:

- Integration of renewable energy systems into facades, such as solar panels and wind turbines.
- Use of smart materials that can adapt to changing weather conditions, optimizing energy consumption.
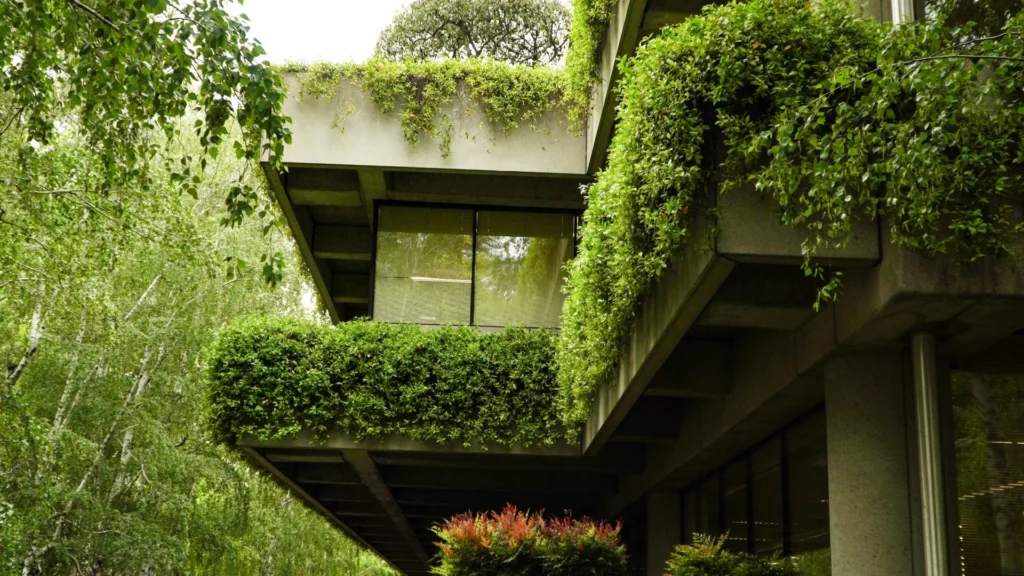
- Incorporation of vertical gardens and green facades, enhancing air quality and aesthetics.
- Integration of interactive components, such as embedded sensors and dynamic lighting systems, creating engaging and interactive facades.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the facade is much more than just the face of a building. It serves as an expression of architectural creativity, an essential protective barrier, and a visual representation of a structure’s identity. From the ancient classical facades to the modern and futuristic designs, facades have evolved and continue to shape the architectural landscape. As innovations in materials and technologies continue to flourish, facades will play an increasingly significant role in sustainable and visually striking buildings. So, the next time you encounter an impressive facade, admire its beauty, and appreciate the intricate thought and craftsmanship that goes into creating it.